I’m going to show you a quick and easy way how to calculate conduit size for cables and wires, no matter where you are.
This method is perfect for double-checking those pesky hand calculations, and it’s a lifesaver when you’re hustling on the job site or strolling through the aisles of Home Depot. Just use our free conduit sizing calculator, and let it do the heavy lifting for you!
Before we dive in, let’s get familiar with the difference between a wire and a cable – we’ll be using these terms throughout this guide.
Difference between wires and cables
Many people mix up these two terms, but they’re actually quite distinct.
A wire is a single conductor, usually made of copper or aluminum.
A cable, on the other hand, consists of a group of conductors, or two or more insulated wires bundled together. Picture several insulated wires wrapped in one protective jacket – that’s a cable!
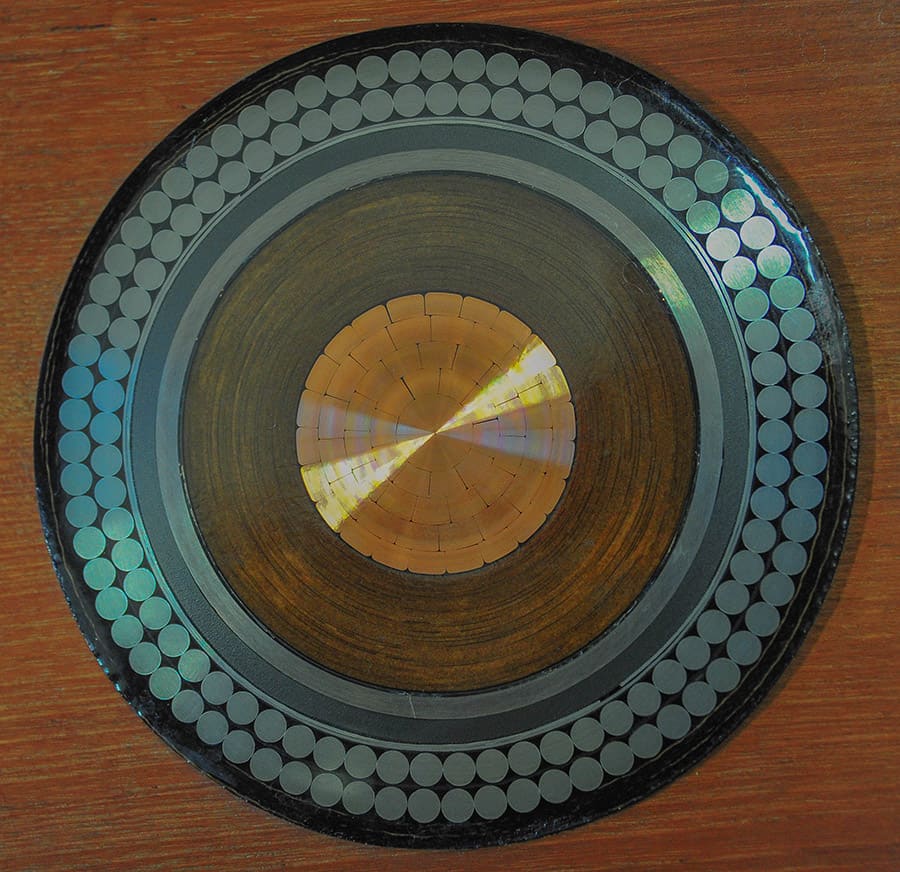

The conventional way how to calculate conduit size for cables and wires
In this example, we’ll size a Schedule 40 PVC conduit for the wires listed below, according to the National Electrical Code (NEC).
| Circuit # | Number of wires | Insulation Type | Gauge |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | THHN | 1/0 KCMIL |
| 2 | 2 | THHN | 4 AWG |
| 3 | 2 | THHN | 8 AWG |
| 4 | 1 | THW | 10 AWG |
| 5 | 1 | XHHW | 12 AWG |
STEP #1: Calculate the wire cross-section area
Using NEC Chapter 9 Table 5, we’ll calculate the cross-section area of each wire. Just match the insulation type to the wire gauge in the NEC table.
| Circuit # | Area (in²) | Number of wires | Total area (in²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1855 | 3 | 0.5565 |
| 2 | 0.0824 | 2 | 0.1648 |
| 3 | 0.0366 | 2 | 0.0732 |
| 4 | 0.0243 | 1 | 0.0243 |
| 5 | 0.0181 | 1 | 0.0181 |
Add up all the wire cross-section areas: 0.5565 + 0.1648 + 0.0732 + 0.0243 + 0.0181 = 0.8369 in²
STEP #2: Finding the minimum available conduit space
We need to figure out how much space our wires can occupy inside a conduit. NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 gives us these guidelines:
- 1 wire: maximum fill is 53% of the total space inside a conduit
- 2 wires: maximum fill is 31% of the total space inside a conduit
- Over 2 wires: maximum fill is 40% of the total space inside a conduit
In our example, we have 9 wires, so we can’t exceed a 40% fill in our conduit.
STEP #3: Determine the conduit size
Using NEC Chapter 9 Table 1, let’s find the conduit size that meets the NEC 40% fill requirement. We’ll search the Schedule 40 PVC conduit table using the total cross-section wire area we calculated earlier.
According to the NEC table, a 2-inch conduit can hold 1.316 in² of fill while staying below the 40% requirement. This works for us since our total wire cross-section area is 0.8459 in².
A smaller conduit size of 1-1/2″ only allows for a fill of 0.794 in², which isn’t enough for our total wire cross-section area of 0.8459 in². So, we’ll stick with the 2-inch conduit!
The quick and easy way how to calculate conduit size for cables and wires
Now, let’s discover how to use our handy conduit sizing calculator, using our original example. You’ll see just how much time and effort you’ll save. Plus, you can easily adjust your conduit fill on the fly to test out various scenarios instantly.
STEP #1: Meet the Conduit Sizing Calculator
Head over to our conduit sizing calculator to kick things off.
STEP #2: Initial inputs
Choose your conduit type from the dropdown menu.
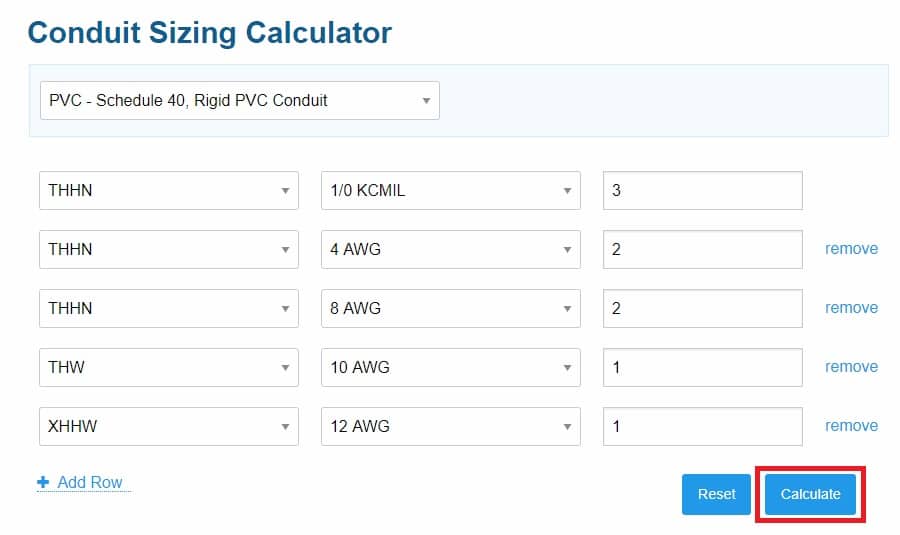
Next, pick your first conductor type and size. After that, enter the conductor count for your first conductor.
In the screenshot below, I’ve plugged in our Circuit #1 values from our example. The calculator then automatically finds and uses the appropriate wire cross-section area.

Calculator tip: Got a custom cable or conductor you want to use? No problem! In the “Select Cable / Conductor Type” field, choose “Other / Custom.” Then enter your cable or conductor cross-section area in square inches.
Often, you’ll use a cable or conductor not documented in the NEC, so you won’t find it in our database.
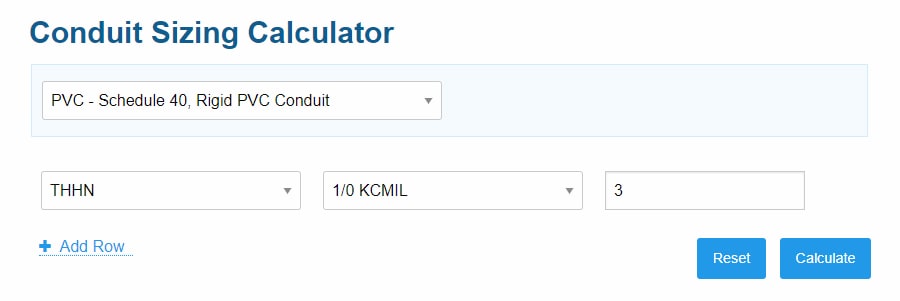
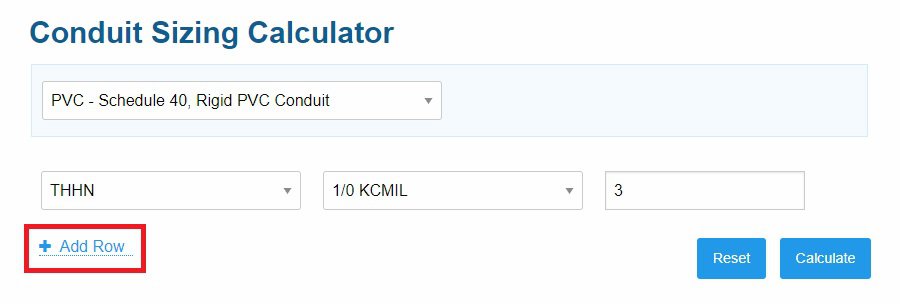
STEP #3: Add More Wires
Click “Add Row” for each extra wire type you want to put inside your conduit.
For our example, we have 5 wire types in total. So, you’ll need to hit the “Add Row” button 4 times.
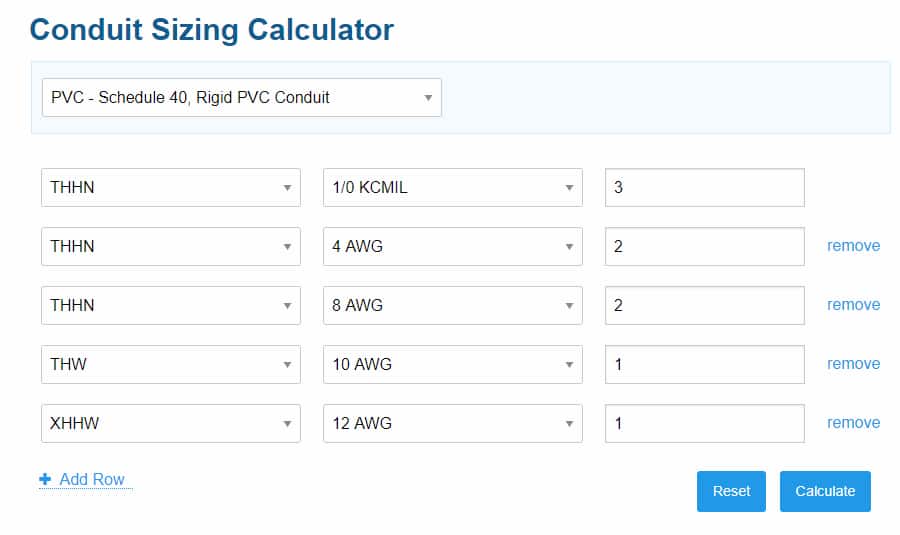
STEP #4: Fill in the Wire Details
Repeat Step #2 for each wire type. Input all your wire information one by one.

Calculator tip: If you accidentally add an extra row, no worries! Just hit the “remove” button at the far right of each row.
STEP #5: Calculate the conduit fill
Now, simply click the “Calculate” button, and voila! You’ve got your conduit size.

Calculator tip: You can still tweak your inputs after hitting “Calculate.” Just press “Calculate” again to see your refreshed results in a snap.
STEP #6: Output results
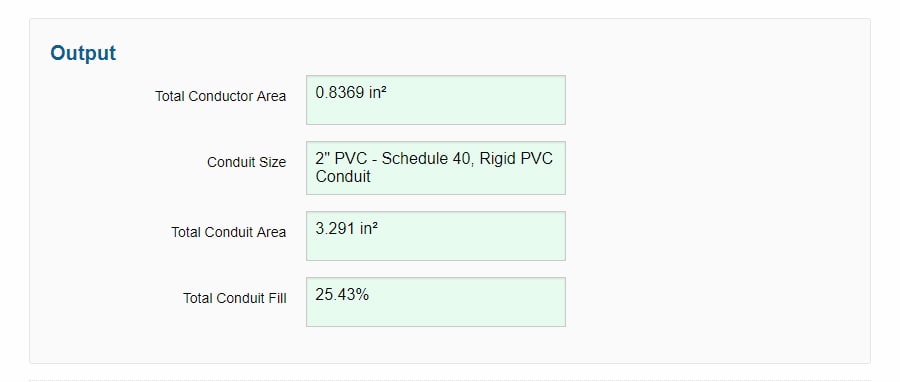
After hitting “Calculate,” scroll down to view your output results. Here, you’ll find all the info on your calculated conduit and wire. The output results include:
- Total Conductor Area: The total conductor cross-section area of all your entered wires.
- Conduit Size: The minimum conduit size allowed by the NEC.
- Total Conduit Area: The total cross-section area of your chosen conduit size.
- Total Conduit Fill: The percentage fill of your selected conduit size based on your total wire cross-section area. In our example, the conduit fill comes out to 25.43%—well below the required 40%. In other words, all the wires combined occupy just 25.43% of the total 2-inch conduit cross-section area.
Comparing our output results
We discovered our calculated total wire cross-section area of 0.8369 in² and 2″ conduit size, lines up with the hand calculations.
The sweet part is, you saved a ton of time. If nothing else, this calculator is a fantastic way to double-check your hand calculation results.
Plus, it lets you play around with different conduit-fill scenarios without tearing your hair out. All while making sure you’re following the NEC guidelines.
Conclusion
We’d love to hear your suggestions for new features or any feedback on how we can improve. Our ultimate goal is to make calculating conduit sizes for cables and wires a breeze for everyone.
So tell us, how do you usually calculate conduit sizes for cables?

Your calculator is not working
It’s working now – check it out!